+7(343)3794350
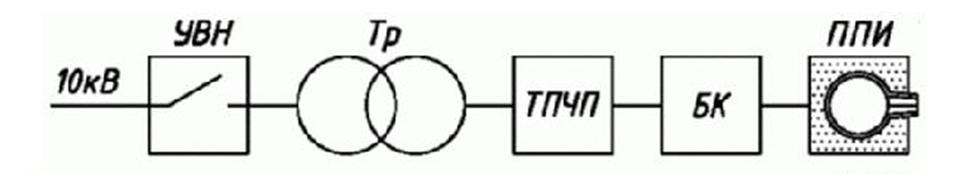
Power supply systems

There are several power supply systems that can consist of different sets of electric equipment and have different numbers of furnaces. The following diagrams show several functional systems with differences in productivity and costs (investments are the most effective when twin-power dual-trak system is used).
CU – capacitor unit
R – rectifier
TH – throttle
I – inverter
IMF – induction melting furnace
PSD – power shifting device
SCR FC – SCR frequency converter
PT – power transformer
HVIU – high voltage input unit
When IMF1 and IMF2 operate by turn, the processing ratio improves because of dead time reducing. However the productivity of such system does not increase significantly in comparison with single-furnace melting system.
The tandem-type two-furnaces melting system with one main electric supply channel and an additional low power electric supply channel enables to raise the efficiency significantly (by about 20%). This happens because SCR FC 1 operates at full power switching from one furnace to another. SCR FC 1 operates with high processing ratio that is almost equal to 1. During holding and melting time an additional low power electric supply channel is connected to the furnaces. The installed power of SCR FC 2 is not more than 10% compared with a main channel power.
The great advantage of a melting system with dual-track frequency converter is the absence of an expensive power shifting device and costs for its maintenance. In such a system there are no work gaps, necessary for switching of a power shifting device. In comparison with one-furnace melting system the price for this system increases by 8% and the productivity increases by 20-25%. So the efficiency of investments increases by 12-15% and such efficiency is the highest among the other melting systems.